On 1st April 2018, the e way bills system was introduced for inter-state movement of goods under GST. Subsequently, the GST e way bills were introduced by all the states for intra-state movement of goods and New Delhi was the last state to introduce the E-Way bill for intra-state movement of goods on 16th June 2018.
As per Rule 138A of CGST Rule, 2017, the driver/conductor of a conveyance who is transporting goods by road through truck/lorry etc. has to compulsorily accompany e way bills when he is transporting goods.
A closer look at the rule 138A makes it clear that carrying an E-way bill is compulsory i.e., in case of movement of goods by road, say through Goods Transport Agency (GTA) or Courier of a consignment value exceeding Rs. 50,000.
What if there is a transportation of goods by the road where the e way bills are not generated
Then in that scenario, a penalty under Section 129* will be attracted.
In other words, if the consignor/consignee/transporter forgot to generate when it is compulsory, then provisions of Section 129* will be attracted.
As we know, the E-way bill has two parts, Part A and Part B, Part A contains the invoice/bill of supply/delivery challan and Part B contains the details of conveyance in which goods are being transported. As per Explanation 2 to R 138(3), generating Part B of the e way bills is compulsory i.e., only filling the information in Part A will not give rise to a valid e-way bill for the movement of goods by road. Meaning thereby that, the penalty under Section 129* will still be attracted for not generating Part-B of the e-way bill.
Here, it is appropriate to discuss provisions of Rule 138(9). Rule 138(9) states that the e-way bill can be cancelled but only within 24 hours of generating the same. In other words, if there is a discrepancy in the information furnished in the e-way bill as against the actual invoice or actual details of the movement of goods, then the e-way bill may be cancelled within 24 hours of its generation.
But having said that there is a provision in rule 138B which states that if the goods or conveyance are verified by a proper officer during transit then in that scenario, an e-way bill cannot be cancelled.
Further as per proviso to Rule 138(10), suppose due to any reason like breakage of conveyance or some obstruction in road movement the goods cannot be delivered within the validity of the e-way bill, the owner of the goods can extend the validity of e-way bill within 8 hours from its expiry. Take, for example, a truck broke down at 8 P.M. on Wednesday, 27th July 2022 and the e-way bill is getting expires at 12 P.M. on Wednesday, 27th July 2022, then in that scenario, the e way bills expiry can be extended till 8 A.M. after providing reason of the same on the e way bills login portal.
Penalty under Sec 129 of the CGST Act, 2017 [As amended by FA, 2021, w.e.f. 1-1-2022]
Sec 129 covers penalty under two situations, first if the owner of the goods comes forward and wants to release the goods and conveyance which have been detained or seized during transit on payment of a penalty and second if the owner of the goods does not come forward. Still, some other person comes forward to get the goods and conveyance released on payment of penalty.
First Scenario i.e, owner of the goods comes forward and wants to release the goods on payment of the penalty, then the penalty of 200% of tax payable on such goods is leviable if the goods being transported are taxable and in case of exempted goods, an amount equal to 2% of the value of goods or Rs. 25,000, whichever is less is leviable as penalty.
Second Scenario i.e., the owner of the goods does not come forward and some other person wants to pay penalty and get the goods released. In this case, the penalty amount will be equal to 50% of the value of the goods or 200% of the tax payable, whichever is higher in the case of taxable goods and the amount equal to 5% of the value of the goods or Rs. 25,000, whichever is less, in case of goods which are exempted.
The proper officer shall collect the penalty and release the goods and conveyance or shall release the goods and conveyance on furnishing of security equal to the amount of penalty as detailed above in the two scenarios.
Easily Generate e-Way Bills: https://hylo.biz/easily-generate-e-way-bills/
Visit our blogs: https://hylo.biz/blogs/
Follow us on Medium: https://medium.com/@hylobiz
Reach us: support@hylobiz.com
Conclusion
e-way bill were introduced for the smooth movement of goods, better tracking and to keep a check on tax evasion.
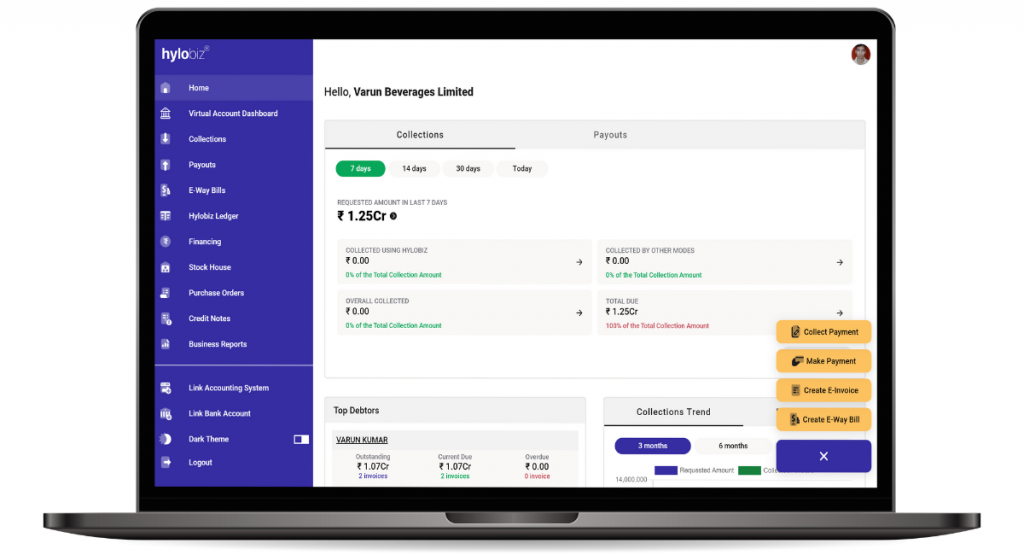
Hylobiz is also helping businesses in managing e-Invoicing and e way bills compliance by providing easy-to-use and user-friendly e way bills and invoice management on its platform. Hylobiz system maintains 100% uptime and is safe and secured. We also provide round-the-clock support from technical and domain experts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) on E way Bills Under GST
- Is it possible that goods are sent by road but an E-way bill is not generated?
As generation and carrying E-way bill in case of movement of goods by road is mandatory as per law, any non-compliance will attract penalty under provisions of Sec 129, if goods and conveyance are inspected during transit. you can easily generate e way bills on Hylobiz with the prefilled data of an invoice.
- Can the E-Way bill be generated after the invoice date?
An e-way bill has to be made before the movement of goods by road. That is to say, the time of generation of the E-Way bill is not linked to the invoice date. Thus, the E-way bill can be generated after the invoice date.
- What is the time gap between invoice date and e-way bill / Can invoice date and e way date be different?
As explained above, the generation of e-way bills is not linked to invoice date rather it is linked with the movement of goods.
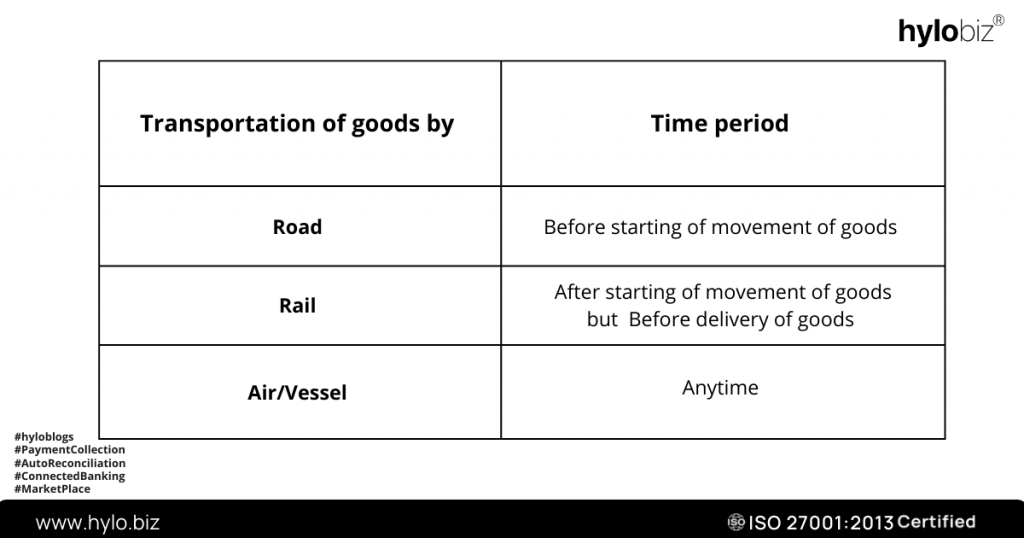
The time limit for issuance of E way bills –
| Transportation of goods by | Time period |
| Road | Before starting of movement of goods |
| Rail | After starting of movement of goods but Before delivery of goods |
| Air/Vessel | Anytime |
- Can we generate an e-way bill after the expiry date?
If the time period for generation of an E-way bill has expired, and goods are not inspected in movement, then in that scenario, an E-way bill can be issued after the expiry period.
- Is there any time gap for updating the Part A and Part B of the E-way bill?
There can be a maximum of 15 days’ time gap between updating Part A and Part B of the E-way bill. After 15 days, Part A of the e-way bill will expire and that e-way bill cannot be generated by filling Part B, and in that scenario, fresh Part A of the E-way bill needs to be filed and submitted.
- Can the goods be seized by the GST authorities even when it is accompanied by Tax Invoice and E-way bill, only on the ambiguity of classification of goods and Tax Tariff?
As per various rulings of high courts, error in the classification of goods is not a valid reason for the seizure of goods by the GST authorities. Thus, authorities can seize goods in non-compliance with provisions of R-138A i.e., non-carrying of invoice/bill of supply and E-way bill.
- How many times can Part B of the E-way bill be updated?
Part B contains the details of conveyance in which goods are being transported. Thus, each time there is a change in conveyance, say, either because of break-down or multi-modal transportation, the information in Part B is to be updated. Further, there is no upper limit on the number of times Part B of the E-way bill can be updated.
- Can I cancel the E-way bill after 72 hours?
As per Rule 138(9), the e-way bill may be cancelled on the common e-way bill portal within 24 hours to generate e way bills.
Thus, one cannot cancel an E-way bill after 72 hours after generation.
- How do I cancel my e way bill after 1 month?
As per discussed in FAQ 8 above, one cannot cancel an E-way bill after 1 month from generation.
